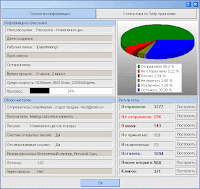
 Largely ignoring its real life applicability, a vendor of "email marketing" tools continues the development of a DIY spamming tools, whose features greatly evolved throughout the last couple of years. Originally released in 2004, the vendor appears to have been actively improving the real-time metrics of the campaigns, next to building interactivity into the spamming process through the WYSIWYG editor.
Largely ignoring its real life applicability, a vendor of "email marketing" tools continues the development of a DIY spamming tools, whose features greatly evolved throughout the last couple of years. Originally released in 2004, the vendor appears to have been actively improving the real-time metrics of the campaigns, next to building interactivity into the spamming process through the WYSIWYG editor.For better or worse, despite that these applications are empowering spammers and lowering down the entry barriers into spamming, the tools have gotten largely replaced by the increasing number of managed spamming services, whose quality assurance features of bypassing spam filters act as a main differentiation factor. Here are some of this tool's features :
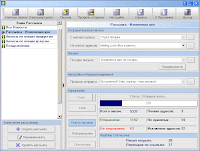 "- High speed distribution - 200,000 letters per hour.
"- High speed distribution - 200,000 letters per hour.- Contains an embedded SMTP server that allows you to send letters directly to the recipient's mailbox without using your provider's SMTP server.
- If you are accessing the Internet via modem, and distribution using the SMTP server, you do not fit - also allowed to send mail through any number of remote SMTP servers (relay), or via SMTP server provider.
- Support for SMTP authentication.
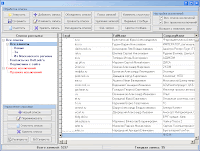 - Supports up to 500 concurrent streams to send to each mailing.
- Supports up to 500 concurrent streams to send to each mailing.- Automatic caching DNS requests to speed up distribution and reducing the load on the DNS server.
- Ability to run multiple independent shots at the same time.
- Ability to suspend delivery and continue later with a point.
- All modes distribution - TO, CC, BCC and PersonalCopy. In the latter case, the program generates a personal letter to each recipient.
 - Ability to specify the size of BCC package regimes TO, CC, and BCC.
- Ability to specify the size of BCC package regimes TO, CC, and BCC.- Ability to specify the TO: field for mailing regimes and CS BCC.
- Full emulation signature letters Outlook Express to increase cross-your-mails through spam filters.
- Support for distribution via a proxy server.
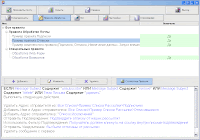
- Automatically detect the bad (non-existent) and not by E-Mail addresses directly in the process of distribution based on a flexible, user SMTP rules. Thanks SMTP rules achieved a very precise definition of bad addresses virtually no false positives.
 - Ability to create lists of addresses, depending on the specific responses of remote servers for SMTP commands.
- Ability to create lists of addresses, depending on the specific responses of remote servers for SMTP commands.- Organize automatically subscribe / unsubscribe to the mailing addresses.
- Perform any processing of existing lists.
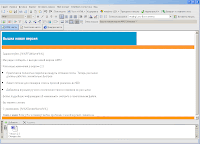
- Develop a letter to the powerful WYSIWYG Html editor.
- Automatically apply to each recipient by name, as well as paste in a letter to a specific, personalized information through powerful Mail Merge templates.
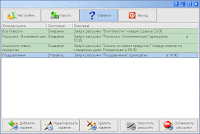 - Set the calendar to automatically launch shots at the right time.
- Set the calendar to automatically launch shots at the right time.- Quickly send out mail."
With managed spam services' on-demand, risk forwarding and completely outsourced processes, they're not only going to replace such DIY tools, but also, position them as a dynamically evolving cybercrime platforms.