 From copycats and "localizers" of Russian web malware exploitation kits, to suppliers of original hacking tools, the Chinese IT underground has been closely following the emerging threats and the obvious insecurities on a large scale, and so is either filling the niches left open by other international communities, or coming up with tools setting new benchmarks for massive SQL injection attacks, like the case with this one :
From copycats and "localizers" of Russian web malware exploitation kits, to suppliers of original hacking tools, the Chinese IT underground has been closely following the emerging threats and the obvious insecurities on a large scale, and so is either filling the niches left open by other international communities, or coming up with tools setting new benchmarks for massive SQL injection attacks, like the case with this one :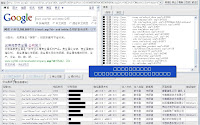 "A professional web site vulnerability scanning, use of tools, SQL injection is a new generation of tools to help Web developers and site of the station quickly find vulnerabilities in order to be able to effectively prepare Security work. At the same time, the tool to Web developers to demonstrate the ways in which hackers are using these vulnerabilities, hackers, as well as through the loopholes to do things, can effectively raise the safety awareness of relevant personnel."
"A professional web site vulnerability scanning, use of tools, SQL injection is a new generation of tools to help Web developers and site of the station quickly find vulnerabilities in order to be able to effectively prepare Security work. At the same time, the tool to Web developers to demonstrate the ways in which hackers are using these vulnerabilities, hackers, as well as through the loopholes to do things, can effectively raise the safety awareness of relevant personnel." Nothing's wrong with the marketing pitch at the first place, but going through the features, the "massive SQL injections through search engine reconnaissance" and automatic page rank verification which you can see in the attached screenshots, ruin the "security auditing" marketing pitch. The tool not only allows easy integration of potentially vulnerable sites obtained through search engines reconnaissance, but also, is prioritizing the results based on the probability for successful injection, next to the page rank of the domains in question. A simple demonstration offered by the company is also, directly enticing its users to "localize" the search engine reconnaissance, by filtering the search results for a particupar country, in this case they used French sites for one of the demos. Here are some excerpts from its CHANGE log speaking for themselves :
Nothing's wrong with the marketing pitch at the first place, but going through the features, the "massive SQL injections through search engine reconnaissance" and automatic page rank verification which you can see in the attached screenshots, ruin the "security auditing" marketing pitch. The tool not only allows easy integration of potentially vulnerable sites obtained through search engines reconnaissance, but also, is prioritizing the results based on the probability for successful injection, next to the page rank of the domains in question. A simple demonstration offered by the company is also, directly enticing its users to "localize" the search engine reconnaissance, by filtering the search results for a particupar country, in this case they used French sites for one of the demos. Here are some excerpts from its CHANGE log speaking for themselves :"2008.7.15 release version 1.3
 - New powerful "automatic machine cycle" feature
- New powerful "automatic machine cycle" feature - Automatic machine cycle is to provide assistance to the advanced user manual into the use of a very
- powerful and flexible module, the main sites used for some special filtering into the hand, is almost a
- universal tool, you can achieve the following:
 1. In support of GET / POST / COOKIES in a variety of ways, such as the injection.
1. In support of GET / POST / COOKIES in a variety of ways, such as the injection. 2. Scan the key to the page (background, upload, WebShell, databases, backup files, etc.).
3. According to the dictionary to violence landing back-guess solution WebShell password and password (required to verify that the code can not guess solution).
4. Page language does not limit the types and databases (to provide specific statements into the database).
5. At the same time, support for the circulation of the two variables and two dictionaries, fast running and violent content of the database solution to guess a password."
It gets even more interesting in terms of the massive SQL injection attacks mentality which is pretty evident on all fronts :
 "- The use of the three search engine sites scans to invade the side to complete
"- The use of the three search engine sites scans to invade the side to complete- in scanning probe into the Web site ranking points
- added, "VBS upload to download", "upload directory Web site viewer," "FTP upload to download configuration file" function to make it more convenient for the sa rights to use the site.
- New "sequence document scanners"
- What is the sequence document scanners role? Upload to find loopholes, some of the procedures to upload the file after the upload will be renamed, rename the way the system is usually based on time or incremental increase in the number prefix code for the upload process, if not to return after the file name, Upload files to know the url is usually very difficult to sequence the use of paper scanner can be scanned out

- The best reverse domain name query engine, and quasi-wide
- in scanning the database of basic information, an increase of the database of information related to the process, the link has information on the database server user login (sa need permission)
- control of the interface had a big adjustment, the interface process easier to understand and operate.
- based on a significant site of the wrong mode of access to a comprehensive code optimization and more accurate access to the content, accuracy and access to show progress.
- added, "VBS upload to download", "upload directory Web site viewer," "FTP upload to download configuration file" function to make it more convenient for the sa rights to use the site.

- point into the types of improved detection order to improve the efficiency of detection.
- improved automatic keyword detection, automatic keyword detection more accurate.
- probe into the points the way to improve and increase the use of automatic detection of the keyword detection.
- type of database to improve the detection, the use of the contents of the length of the failure to detect the type of database automatically switch to the probe through the keyword.
- automatically save and load solution has been to guess the tree structure of the database, guess Solutions has been the content and structure of the database will automatically save and open the next time the injection point will be automatically made available, the solutions do not have to guess again, the continuity of work Greatly increased.

- solved from the database to read large amounts of data (on hundreds of thousands or millions of records), the half-way card program will die.
- increased significantly on the wrong model of ASP.NET and SQL Server2005 significant mode of dealing with mistakes, error messages can be extracted from a Web directory!
- significant amendments to the wrong mode, some of the injected one by one point in the field or access to the contents of the issue can not be successful (error code in hand); for increased access to specific points table and into the field.
- amendments to the text of a significant error patterns to detect and correct use of loopholes in the system can be used more to expand. (Text significantly in the wrong mode in version 1.1 already supported, but in the version 1.2 upgrade in the process of scanning to improve the performance of the Gaodiao careless. -_-#)
- on a variety of encoded text can be significantly wrong in the right-compatible, able to correctly handle the ASP.NET page of the text marked wrong. Through custom error keyword, truly compatible with any language, any coding error message.
- crack anti-improvement and enhancement.
- An increase of auto-detection feature keywords.
- Mssql database specifically for significant points into the wrong mode of detection and the use of up and down the hard work, and many other software can not detect the point of injection can also be used.
- Automatic save and load access to the database, to allow manual known to add tables and fields for solutions to guess.
- Can be used to amend the degree of accuracy; optimize the code to reduce memory footprint; enhance the stability of multi-threading.
- Significant amendments to the wrong mode solution guess the contents of the database must be checked first field defects."
The public version of the tool has been in the while for over an year, with a VIP version available to customers only.

















































